BBC News
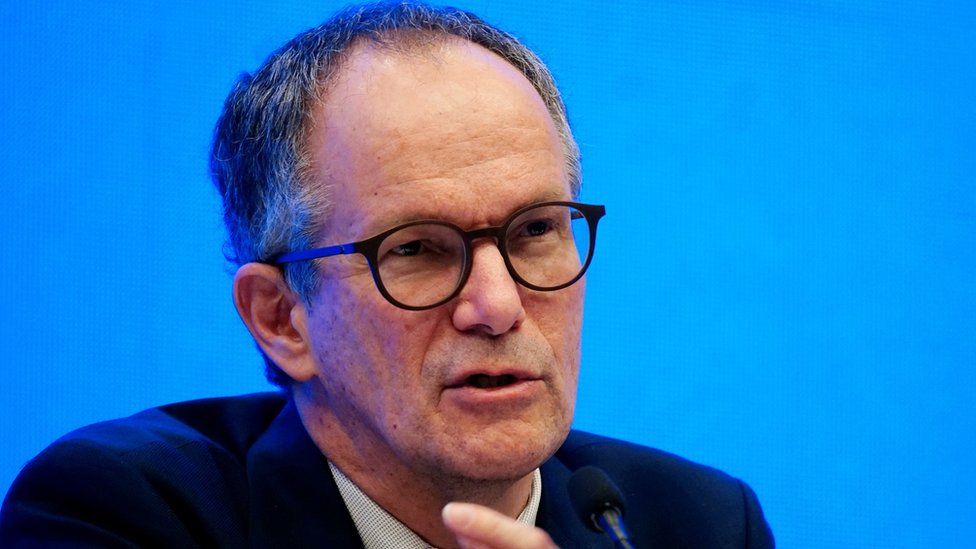 IMAGE COPYRIGHTREUTERS
IMAGE COPYRIGHTREUTERSInternational experts investigating the origins of Covid-19 have all but dismissed a theory that the virus came from a laboratory in China.
Peter Ben Embarek, the head of the World Health Organization (WHO) mission, said it was “extremely unlikely” that the virus leaked from a lab in the city of Wuhan.
He said more work was needed to identify the source of the virus.
The comments came at the conclusion of a joint WHO-China mission.
Wuhan, in China’s central Hubei province, is the first place in the world that the virus was detected. Since then, more than 106 million cases and 2.3 million deaths have been reported worldwide.
Dr Embarek told a press conference the investigation had uncovered new information but had not dramatically changed the picture of the outbreak.
Experts believe the virus is likely to have originated in animals before spreading to humans, but they are not sure how.
Dr Embarek said work to identify the origins of Covid-19 pointed to a “natural reservoir” in bats, but it was unlikely that this happened in Wuhan.
The experts also said there was “no indication” that the virus was circulating in Wuhan before the first official cases were recorded there in December 2019.
Liang Wannian, an expert with China’s Health Commission, said Covid-19 could have been in other regions before it was detected in Wuhan.
The team called for further investigation into the possibility of “cold chain” transmission, referring to the transport and trade of frozen food.
The WHO mission began in January, following months of negotiations with Beijing. The experts’ visit was closely-monitored by the Chinese authorities.

Complicated task

It was unlikely that the expert group, in its politically-charged mission, would be able to pinpoint the source of the pandemic in China a year after it began. But, after visiting the Wuhan Institute of Virology, they have closed the lid on a controversial theory that coronavirus came from a lab leak or was made by scientists.
Their search for clues also included a visit to the now-famous wet market in Huanan – selling fish, meat and live wild animals – that was linked to some of the first human cases.
The team say the virus may have jumped from animals to humans, but they don’t have the proof yet.
Possible carriers include bats and pangolins, but tests so far have yet to find convincing evidence for this. Another line of investigation is whether the virus could have spread through imported frozen food. The hunt for the origin will continue.

What was the laboratory theory?
Speculation about the Wuhan Institute of Virology – one of China’s top virus research labs – began last year and was propagated by former US President Donald Trump.
The office of the US national intelligence director said at the time that while the virus was not man-made or genetically modified, officials were investigating whether the outbreak began through contact with animals or through a laboratory accident.
But Dr Embarek said a visit to the laboratory during the mission showed it was “very unlikely” that anything could have leaked out.
He said the laboratory theory was “not in the hypotheses that we will suggest for future studies”.