The world has experienced rapid urbanization over the last century.
Today, more than 4.3 billion people live in urban settings, or 55% of the world’s population.
But what is the world’s largest city? Answers to that question will vary greatly depending on which lines are being used to demarcate city boundaries and measure their populations.
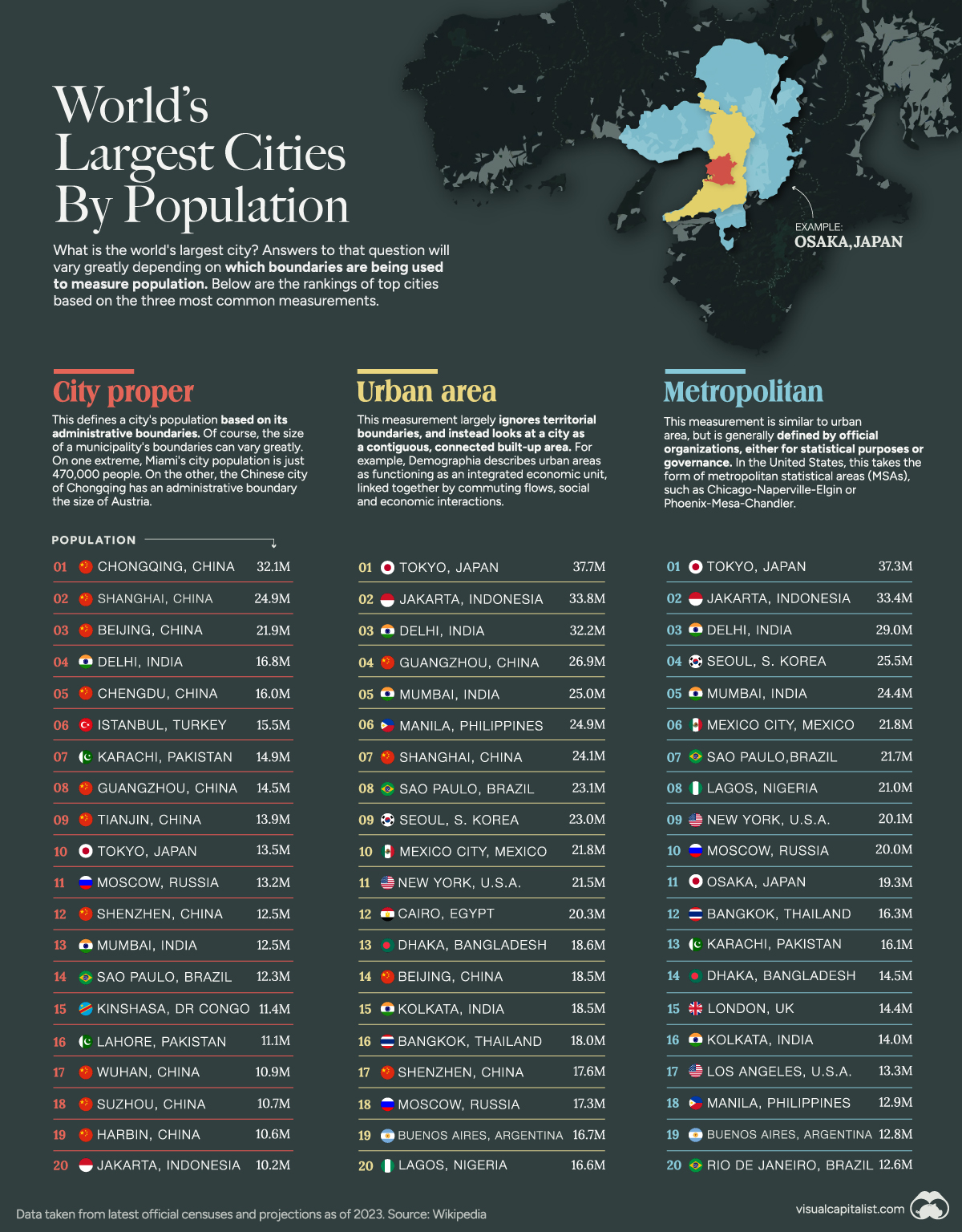
The Largest Cities by City Proper
Our first metric is based on the city proper, meaning the administrative boundaries.
According to the United Nations, a city proper is “the single political jurisdiction which contains the historical city center.”
The Chinese city of Chongqing leads the ranks by this metric and has an administrative boundary the size of Austria, with an urban population of 32.1 million.
The city’s monorail system holds records for being the world’s longest and busiest, boasting 70 stations. Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport, is among the world’s top 50 busiest airports. Additionally, the city ranks among the globe’s top 50 hubs for scientific research.
Other Chinese cities dominate the ranking by this metric:
The United Nations projects India will add over 400 million urban dwellers by 2050, compared to 250 million people in China and 190 million in Nigeria.
The Largest Cities by Urban Area
This measurement largely ignores territorial boundaries and considers a city a contiguous, connected built-up area.
Demographia describes urban areas as functioning as an integrated economic unit, linked by commuting flows, social, and economic interactions.
By this metric, Tokyo leads the ranking:
Consequently, even with one of the world’s largest railway systems, trains in Tokyo are incredibly crowded, with a boarding rate of 200% during peak time in the most overcrowded areas. The city is also famous for its Shibuya Crossing, the busiest intersection on the planet.
The Largest Cities by Metropolitan Area
Tokyo also leads by our final metric, metropolitan area.
This measurement is similar to urban area, but is generally defined by official organizations, either for statistical purposes or governance.
In the United States, this takes the form of metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs), such as Chicago-Naperville-Elgin or Phoenix-Mesa-Chandler.
The UN projects that by 2050, 68% of the world will live in urban areas.