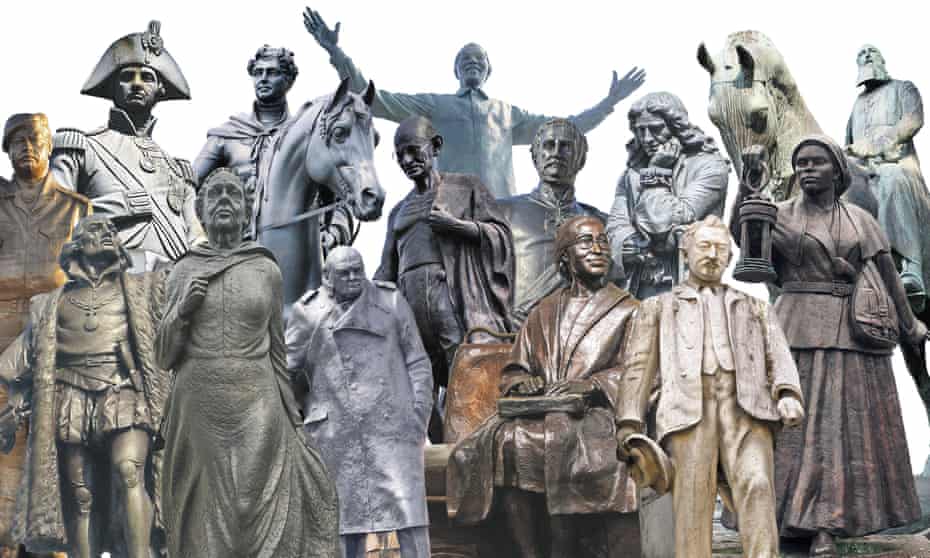
Statues of historical figures are lazy, ugly and distort history. From Cecil Rhodes to Rosa Parks, let’s get rid of them all
Having been a black leftwing Guardian columnist for more than two decades, I understood that I would be regarded as fair game for the kind of moral panics that might make headlines in rightwing tabloids. It’s not like I hadn’t given them the raw material. In the course of my career I’d written pieces with headlines such as “Riots are a class act”, “Let’s have an open and honest conversation about white people” and “End all immigration controls”. I might as well have drawn a target on my back. But the only time I was ever caught in the tabloids’ crosshairs was not because of my denunciations of capitalism or racism, but because of a statue – or to be more precise, the absence of one.
The story starts in the mid-19th century, when the designers of Trafalgar Square decided that there would be one huge column for Horatio Nelson and four smaller plinths for statues surrounding it. They managed to put statues on three of the plinths before running out of money, leaving the fourth one bare. A government advisory group, convened in 1999, decided that this fourth plinth should be a site for a rotating exhibition of contemporary sculpture. Responsibility for the site went to the new mayor of London, Ken Livingstone.
Livingstone, whom I did not know, asked me if I would be on the committee, which I joined in 2002. The committee met every six weeks, working out the most engaged, popular way to include the public in the process. I was asked if I would chair the meetings because they wanted someone outside the arts and I agreed. What could possibly go wrong?
Well, the Queen Mother died. That had nothing to do with me. Given that she was 101 her passing was a much anticipated, if very sad, event. Less anticipated was the suggestion by Simon Hughes, a Liberal Democrat MP and potential candidate for the London mayoralty, that the Queen Mother’s likeness be placed on the vacant fourth plinth. Worlds collided.
The next day, the Daily Mail ran a front page headline: “Carve her name in pride – Join our campaign for a statue of the Queen Mother to be erected in Trafalgar Square (whatever the panjandrums of political correctness say!)” Inside, an editorial asked whether our committee “would really respond to the national mood and agree a memorial in Trafalgar Square”.
Never mind that a committee, convened by parliament, had already decided how the plinth should be filled. Never mind that it was supposed to be an equestrian statue and that the Queen Mother will not be remembered for riding horses. Never mind that no one from the royal family or any elected official had approached us.
The day after that came a double-page spread headlined “Are they taking the plinth?”, alongside excerpts of articles I had written several years ago, taken out of context, under the headline “The thoughts of Chairman Gary”. Once again the editorial writers were upon us: “The saga of the empty plinth is another example of the yawning gap between the metropolitan elite hijacking this country and the majority of ordinary people who simply want to reclaim Britain as their own.”
The Mail’s quotes were truer than it dared imagine. It called on people to write in, but precious few did. No one was interested in having the Queen Mother in Trafalgar Square. The campaign died a sad and pathetic death. Luckily for me, it turned out that, if there was a gap between anyone and the ordinary people of the country on this issue, then the Daily Mail was on the wrong side of it.
This, however, was simply the most insistent attempt to find a human occupant for the plinth. Over the years there have been requests to put David Beckham, Bill Morris, Mary Seacole, Benny Hill and Paul Gascoigne up there. None of these figures were particularly known for riding horses either. But with each request I got, I would make the petitioner an offer: if you can name those who occupy the other three plinths, then the fourth is yours. Of course, the plinth was not actually in my gift. But that didn’t matter because I knew I would never have to deliver. I knew the answer because I had made it my business to. The other three were Maj Gen Sir Henry Havelock, who distinguished himself during what is now known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857, when an uprising of thousands of Indians ended in slaughter; Gen Sir Charles Napier, who crushed a rebellion in Ireland and conquered the Sindh province in what is now Pakistan; and King George IV, an alcoholic, debtor and womaniser.
The petitioners generally had no idea who any of them were. And when they finally conceded that point, I would ask them: “So why would you want to put someone else up there so we could forget them? I understand that you want to preserve their memory. But you’ve just shown that this is not a particularly effective way to remember people.”
In Britain, we seem to have a peculiar fixation with statues, as we seek to petrify historical discourse, lather it in cement, hoist it high and insist on it as a permanent statement of fact, culture, truth and tradition that can never be questioned, touched, removed or recast. This statue obsession mistakes adulation for history, history for heritage and heritage for memory. It attempts to detach the past from the present, the present from morality, and morality from responsibility. In short, it attempts to set our understanding of what has happened in stone, beyond interpretation, investigation or critique.
But history is not set in stone. It is a living discipline, subject to excavation, evolution and maturation. Our understanding of the past shifts. Our views on women’s suffrage, sexuality, medicine, education, child-rearing and masculinity are not the same as they were 50 years ago, and will be different again in another 50 years. But while our sense of who we are, what is acceptable and what is possible changes with time, statues don’t. They stand, indifferent to the play of events, impervious to the tides of thought that might wash over them and the winds of change that swirl around them – or at least they do until we decide to take them down.
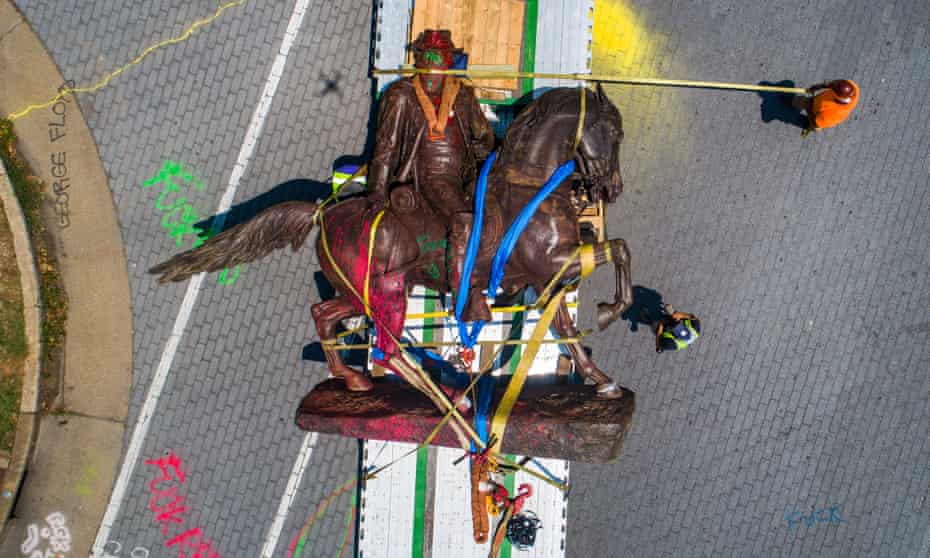

In recent months, I have been part of a team at the University of Manchester’s Centre on the Dynamics of Ethnicity (Code) studying the impact of the Black Lives Matter movement on statues and memorials in Britain, the US, South Africa, Martinique and Belgium. Last summer’s uprisings, sparked by the police murder of George Floyd in Minneapolis, spread across the globe. One of the focal points, in many countries, was statues. Belgium, Brazil, Ireland, Portugal, the Netherlands and Greenland were just a few of the places that saw statues challenged. On the French island of Martinique, the statue of Joséphine de Beauharnais, who was born to a wealthy colonial family on the island and later became Napoleon’s first wife and empress, was torn down by a crowd using clubs and ropes. It had already been decapitated 30 years ago.
Across the US, Confederate generals fell, were toppled or voted down. In the small town of Lake Charles, Louisiana, nature presented the local parish police jury with a challenge. In mid-August last year, the jury voted 10-4 to keep a memorial monument to the soldiers who died defending the Confederacy in the civil war. Two weeks later, Hurricane Laura blew it down. Now the jury has to decide not whether to take it down, but whether to put it back up again.
And then, of course, in Britain there was the statue of Edward Colston, a Bristol slave trader, which ended up in the drink. Britain’s major cities, including Manchester, Glasgow, Birmingham and Leeds, are undertaking reviews of their statues.
Many spurious arguments have been made about these actions, and I will come to them in a minute. But the debate around public art and memorialisation, as it pertains to statues, should be engaged not ducked. One response I have heard is that we should even out the score by erecting statues of prominent black, abolitionist, female and other figures that are underrepresented. I understand the motivation. To give a fuller account of the range of experiences, voices, hues and ideologies that have made us what we are. To make sure that public art is rooted in the lives of the whole public, not just a part of it, and that we all might see ourselves in the figures that are represented.
But while I can understand it, I do not agree with it. The problem isn’t that we have too few statues, but too many. I think it is a good thing that so many of these statues of pillagers, plunderers, bigots and thieves have been taken down. I think they are offensive. But I don’t think they should be taken down because they are offensive. I think they should be taken down because I think all statues should be taken down.
Here, to be clear, I am talking about statues of people, not other works of public memorials such as the Vietnam Veterans Memorial in Washington DC, the Holocaust memorial in Berlin or the Famine memorial in Dublin. I think works like these serve the important function of public memorialisation, and many have the added benefit of being beautiful.
The same cannot be said of statues of people. I think they are poor as works of public art and poor as efforts at memorialisation. Put more succinctly, they are lazy and ugly. So yes, take down the slave traders, imperial conquerors, colonial murderers, warmongers and genocidal exploiters. But while you’re at it, take down the freedom fighters, trade unionists, human rights champions and revolutionaries. Yes, remove Columbus, Leopold II, Colston and Rhodes. But take down Mandela, Gandhi, Seacole and Tubman, too.
I don’t think those two groups are moral equals. I place great value on those who fought for equality and inclusion and against bigotry and privilege. But their value to me need not be set in stone and raised on a pedestal. My sense of self-worth is not contingent on seeing those who represent my viewpoints, history and moral compass forced on the broader public. In the words of Nye Bevan, “That is my truth, you tell me yours.” Just be aware that if you tell me your truth is more important than mine, and therefore deserves to be foisted on me in the high street or public park, then I may not be listening for very long.
For me the issue starts with the very purpose of a statue. They are among the most fundamentally conservative – with a small c – expressions of public art possible. They are erected with eternity in mind – a fixed point on the landscape. Never to be moved, removed, adapted or engaged with beyond popular reverence. Whatever values they represent are the preserve of the establishment. To put up a statue you must own the land on which it stands and have the authority and means to do so. As such they represent the value system of the establishment at any given time that is then projected into the forever.
That is unsustainable. It is also arrogant. Societies evolve; norms change; attitudes progress. Take the mining magnate, imperialist and unabashed white supremacist Cecil Rhodes. He donated significant amounts of money with the express desire that he be remembered for 4,000 years. We’re only 120 years in, but his wish may well be granted. The trouble is that his intention was that he would be remembered fondly. And you can’t buy that kind of love, no matter how much bronze you lather it in. So in both South Africa and Britain we have been saddled with these monuments to Rhodes.
The trouble is that they are not his only legacy. The systems of racial subjugation in southern Africa, of which he was a principal architect, are still with us. The income and wealth disparities in that part of the world did not come about by bad luck or hard work. They were created by design. Rhodes’ design. This is the man who said: “The native is to be treated as a child and denied franchise. We must adopt a system of despotism, such as works in India, in our relations with the barbarism of South Africa.” So we should not be surprised if the descendants of those so-called natives, the majority in their own land, do not remember him fondly.
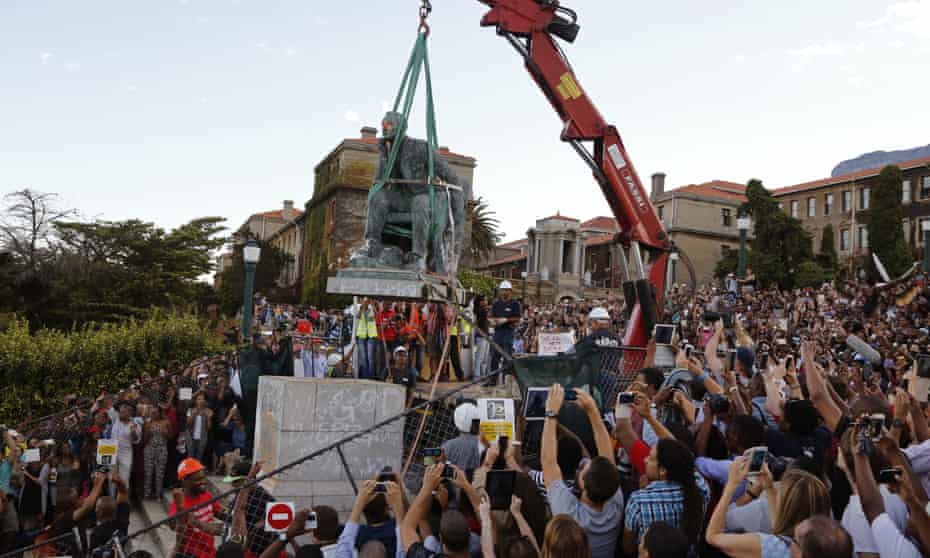
A similar story can be told in the southern states of the US. In his book Standing Soldiers, Kneeling Slaves, the American historian Kirk Savage writes of the 30-year period after the civil war: “Public monuments were meant to yield resolution and consensus, not to prolong conflict … Even now to commemorate is to seek historical closure, to draw together the various strands of meaning in an historical event or personage and condense its significance.”
Clearly these statues – of Confederate soldiers in the South, or of Rhodes in South Africa and Oxford – do not represent a consensus now. If they did, they would not be challenged as they are. Nobody is seriously challenging the statue of the suffragist Millicent Fawcett in Parliament Square, because nobody seriously challenges the notion of women’s suffrage. Nor is anyone seeking historical closure via the removal of a statue. The questions that some of these monuments raise – of racial inequality, white supremacy, imperialism, colonialism and slavery – are still very much with us. There is a reason why these particular statues, and not, say, that of Robert Raikes, who founded Sunday schools, which stands in Victoria Embankment Gardens in London, were targeted during the Black Lives Matter protests.
But these statues never represented a consensus, even when they were erected. Take the statues of Confederate figures in Richmond, Virginia that were the focus of protests last summer. Given that the statues represented men on the losing side of the civil war, they certainly didn’t represent a consensus in the country as a whole. The northern states wouldn’t have appreciated them. But closer to home, they didn’t even represent the general will of Richmond at the time. The substantial African American population of the city would hardly have been pleased to see them up there. And nor were many whites, either. When a labour party took control of Richmond city council in the late 1880s, a coalition of blacks and working-class whites refused to vote for an unveiling parade for the monument because it would “benefit only a certain class of people”.
Calls for the removal of statues have also raised the charge that longstanding works of public art are at the mercy of political whim. “Is nothing sacred?” they cry. “Who next?” they ask, clutching their pearls and pointing to Churchill. But our research showed these statues were not removed as a fad or in a feverish moment of insubordination. People had been calling for them to be removed for half a century. And the issue was never confined to the statue itself. It was always about what the statue represented: the prevailing and persistent issues that remained, and the legacy of whatever the statue was erected to symbolise.
One of the greatest distractions when it comes to removing statues is the argument that to remove a statue is to erase history; that to change something about a statue is to tamper with history. This is such arrant nonsense it is difficult to know where to begin, so I guess it would make sense to begin at the beginning.
Statues are not history; they represent historical figures. They may have been set up to mark a person’s historical contribution, but they are not themselves history. If you take down Nelson Mandela’s bust on London’s South Bank, you do not erase the history of the anti-apartheid struggle. Statues are symbols of reverence; they are not symbols of history. They elevate an individual from a historical moment and celebrate them.
Nobody thinks that when Iraqis removed statues of Saddam Hussein from around the country they wanted him to be forgotten. Quite the opposite. They wanted him, and his crimes, to be remembered. They just didn’t want him to be revered. Indeed, if the people removing a statue are trying to erase history, then they are very bad at it. For if the erection of a statue is a fact of history, then removing it is no less so. It can also do far more to raise awareness of history. More people know about Colston and what he did as a result of his statue being taken down than ever did as a result of it being put up. Indeed, the very people campaigning to take down the symbols of colonialism and slavery are the same ones who want more to be taught about colonialism and slavery in schools. The ones who want to keep them up are generally the ones who would prefer we didn’t study what these people actually did.
But to claim that statues represent history does not merely misrepresent the role of statues, it misunderstands history and their place in it. Let’s go back to the Confederate statues for a moment. The American civil war ended in 1865. The South lost. Much of its economy and infrastructure were laid to waste. Almost one in six white Southern men aged 13 to 43 died; even more were wounded; more again were captured.
Southerners had to forget the reality of the civil war before they could celebrate it. They did not want to remember the civil war as an episode that brought devastation and humiliation. Very few statues went up in the decades immediately after the war. According to the Southern Poverty Law Centre, almost 500 monuments to the Confederate cause went up between 1885 and 1915. More than half were built within one seven-year period, between 1905 and 1912.
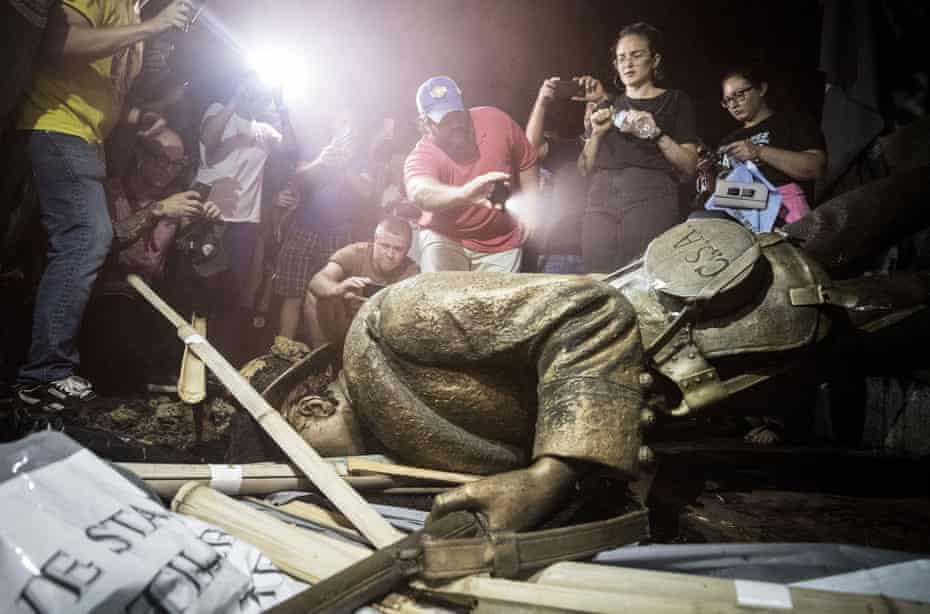

The timing was no coincidence. It was long enough since the horrors of the civil war that it could be misremembered as a noble defence of racialised regional culture rather than just slavery. As such, it represented a sanitised, partial and selective version of history, based less in fact than toxic nostalgia and melancholia. It’s not history that these statues’ protectors are defending: it’s mythology.
Colston, an official in the Royal African Company, which reportedly sold as many as 100,000 west Africans into slavery, died in 1721. His statue didn’t go up until 1895, more than 150 years later. This was no coincidence, either. Half of the monuments contested over the past year were erected between 1889 and 1919. This was partly an aesthetic trend of the late Victorian era. But it should probably come as little surprise that the statues that anti-racist protesters wanted to be taken down were those erected when Jim Crow segregation was firmly installed in the US, and at the apogee of colonial expansion.
Statues always tell us more about the values of the period when they were put up than about the story of the person depicted. Two years before Martin Luther King’s death, a poll showed that the majority of Americans viewed him unfavourably. Four decades later, when Barack Obama unveiled a memorial to King in Washington DC, 91% of Americans approved. Rather than teaching us about the past, his statue distorts history. As I wrote in my book The Speech: The Story Behind Dr Martin Luther King Jr’s Dream, “White America came to embrace King in the same way that white South Africans came to embrace Nelson Mandela: grudgingly and gratefully, retrospectively, selectively, without grace or guile. Because by the time they realised their hatred of him was spent and futile, he had created a world in which loving him was in their own self-interest. Because, in short, they had no choice.”
One claim for not bringing down certain statues of people who committed egregious acts is that we should not judge people of another time by today’s standards. I call this the “But that was before racism was bad” argument or, as others have termed it, the Jimmy Savile defence.
Firstly, this strikes me as a very good argument for not erecting statues at all, since there is no guarantee that any consensus will persist. Just because there may be a sense of closure now doesn’t mean those issues won’t one day be reopened. But beyond that, by the time many of these statues went up there was already considerable opposition to the deeds that had made these men (and they are nearly all men) rich and famous. In Britain, slavery had been abolished more than 60 years before Colston’s statue went up. The civil war had been over for 30 years before most statues of Confederate generals went up. Cecil Rhodes and King Leopold II of Belgium were both criticised for their vile racist acts and views by their contemporaries. In other words, not only was what they did wrong, but it was widely known to be wrong at the time they did it. By the time they were set in stone there were significant movements, if not legislation, condemning the very things that had made them rich and famous.

A more honest appraisal of why the removal of these particular statues rankles with so many is that they do not actually want to engage with the history they represent. Power, and the wealth that comes with it, has many parents. But the brutality it takes to acquire it is all too often an orphan. According to a YouGov poll last year, only one in 20 Dutch, one in seven French, one in 5 Brits and one in four Belgians and Italians believe their former empire is something to be ashamed of. If these statues are supposed to tell our story, then why, after more than a century, do so few people actually know it?
This brings me to my final point. Statues do not just fail to teach us about the past, or give a misleading idea about particular people or particular historical events – they also skew how we understand history itself. For when you put up a statue to honour a historical moment, you reduce that moment to a single person. Individuals play an important role in history. But they don’t make history by themselves. There are always many other people involved. And so what is known as the Great Man theory of history distorts how, why and by whom history is forged.
Consider the statue of Rosa Parks that stands in the US Capitol. Parks was a great woman, whose refusal to give up her seat for a white woman on a bus in Montgomery, Alabama challenged local segregation laws and sparked the civil rights movement. When Parks died in 2005, her funeral was attended by thousands, and her contribution to the civil rights struggle was eulogised around the world.
But the reality is more complex. Parks was not the first to plead not guilty after resisting Montgomery’s segregation laws on its buses. Before Parks, there was a 15-year-old girl named Claudette Colvin. Colvin was all set to be the icon of the civil rights movement until she fell pregnant. Because she was an unmarried teenager, she was dropped by the conservative elders of the local church, who were key leaders of the movement. When I interviewed Colvin 20 years ago, she was just getting by as a nurses’ aide and living in the Bronx, all but forgotten.
And while what Parks did was a catalyst for resistance, the event that forced the segregationists to climb down wasn’t the work of one individual in a single moment, but the year-long collective efforts of African Americans in Montgomery who boycotted the buses – maids and gardeners who walked miles in sun and rain, despite intimidation, those who carpooled to get people where they needed to go, those who sacrificed their time and effort for the cause. The unknown soldiers of civil rights. These are the people who made it happen. Where is their statue? Where is their place in history? How easily and wilfully the main actors can be relegated to faceless extras.
I once interviewed the Uruguayan writer Eduardo Galeano, who confessed that his greatest fear was “that we are all suffering from amnesia”. Who, I asked, is responsible for this forgetfulness? “It’s not a person,” he explained. “It’s a system of power that is always deciding in the name of humanity who deserves to be remembered and who deserves to be forgotten … We are much more than we are told. We are much more beautiful.”
Statues cast a long shadow over that beauty and shroud the complexity even of the people they honour. Now, I love Rosa Parks. Not least because the story usually told about her is so far from who she was. She was not just a hapless woman who stumbled into history because she was tired and wanted to sit down. That was not the first time she had been thrown off a bus. “I had almost a life history of being rebellious against being mistreated against my colour,” she once said. She was also an activist, a feminist and a devotee of Malcolm X. “I don’t believe in gradualism or that whatever should be done for the better should take for ever to do,” she once said.

Of course I want Parks to be remembered. Of course I want her to take her rightful place in history. All the less reason to diminish that memory by casting her in bronze and erecting her beyond memory.
So let us not burden future generations with the weight of our faulty memory and the lies of our partial mythology. Let us not put up the people we ostensibly cherish so that they can be forgotten and ignored. Let us elevate them, and others – in the curriculum, through scholarships and museums. Let us subject them to the critiques they deserve, which may convert them from inert models of their former selves to the complex, and often flawed, people that they were. Let us fight to embed the values of those we admire in our politics and our culture. Let’s cover their anniversaries in the media and set them in tests. But the last thing we should do is cover their likeness in concrete and set them in stone.
Additional reporting by Meghan Tinsley, Ruth Ramsden-Karelse, Chloe Peacock and Sadia Habib. Gary Younge is a professor of sociology at the University of Manchester and a Type Media Fellow. He delivers the annual Aneurin Bevan Lecture at Hay Festival 2021, free online this Friday 4 June at 2pm. Explore the full festival programme and register now at hayfestival.org/wales









